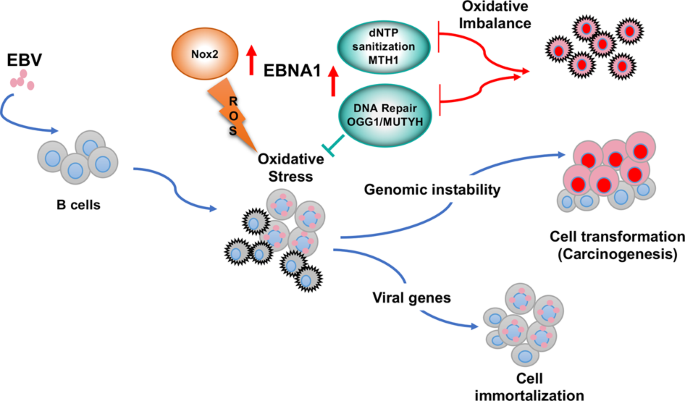
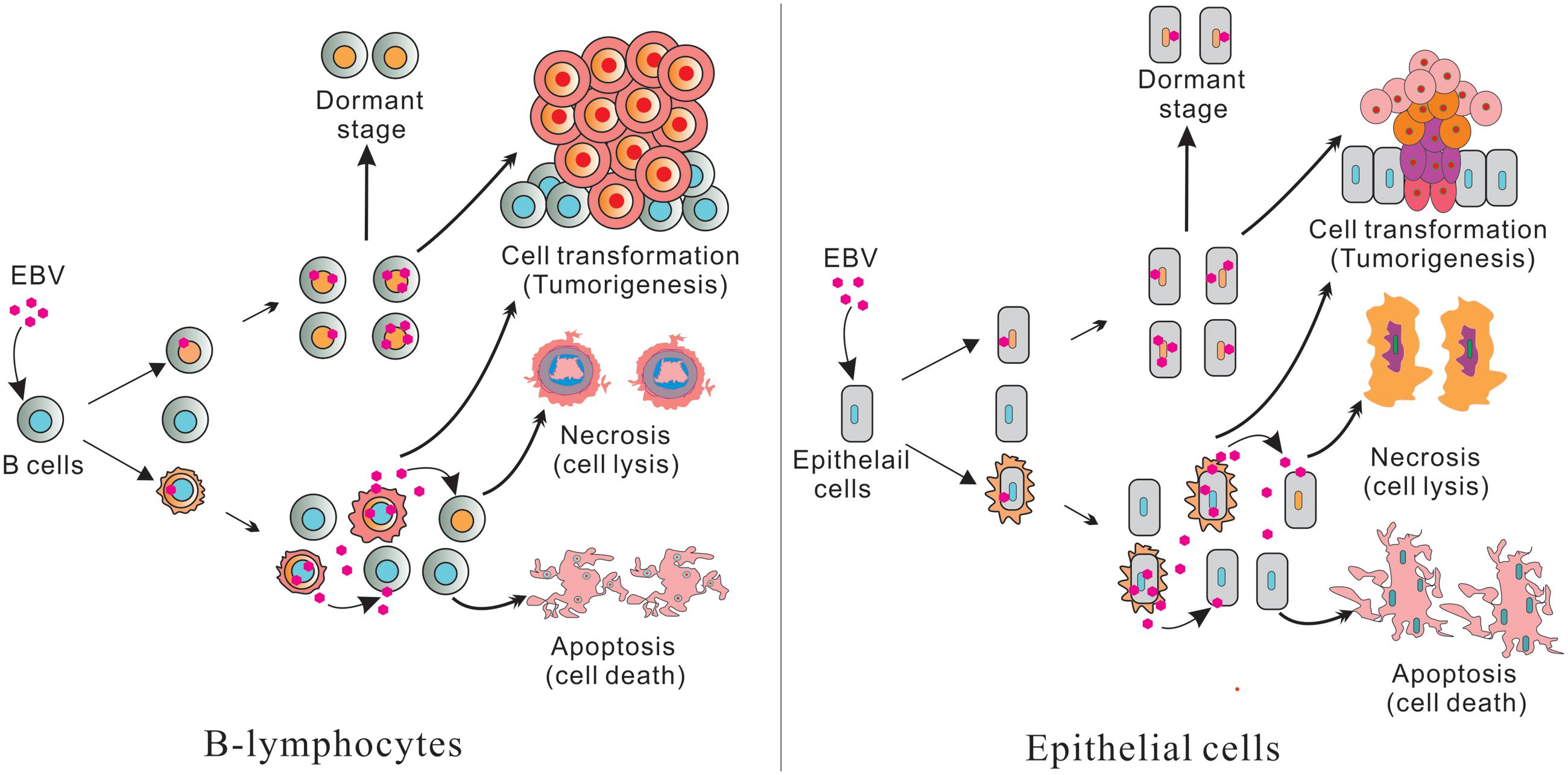
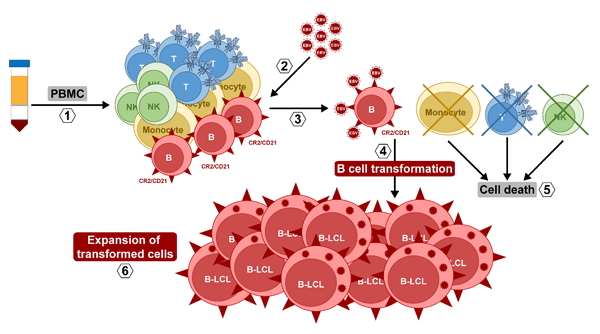
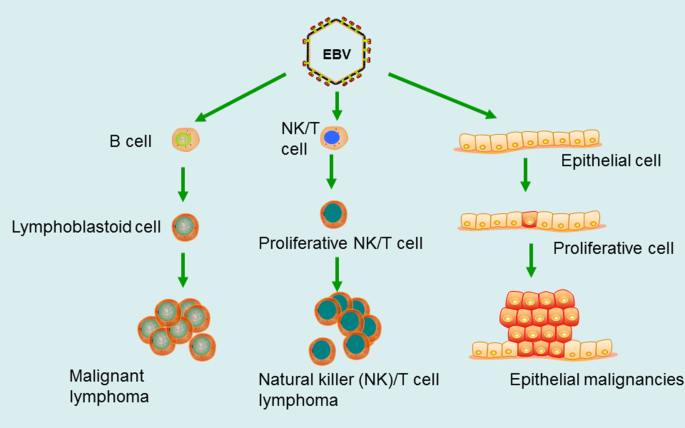
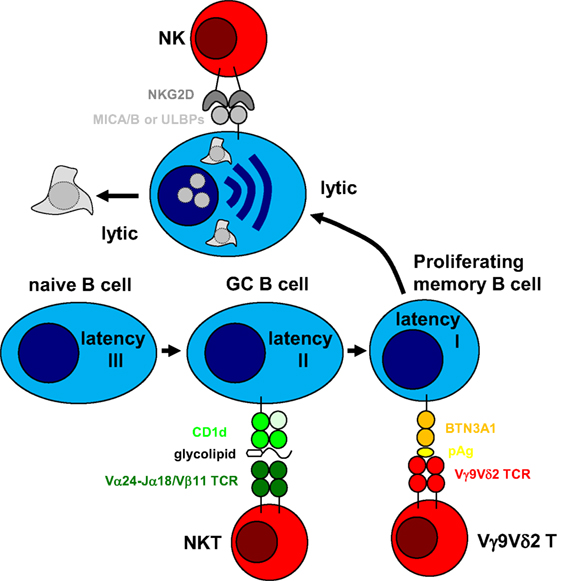
EBV Latency III–Transformed B Cells Are Inducers of Conventional and Unconventional Regulatory T Cells in a PD-L1–Dependent Manner | The Journal of Immunology
Spontaneous lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with Epstein-Barr virus infection show highly variable proliferation characteristics that correlate with the expression levels of viral microRNAs | PLOS ONE
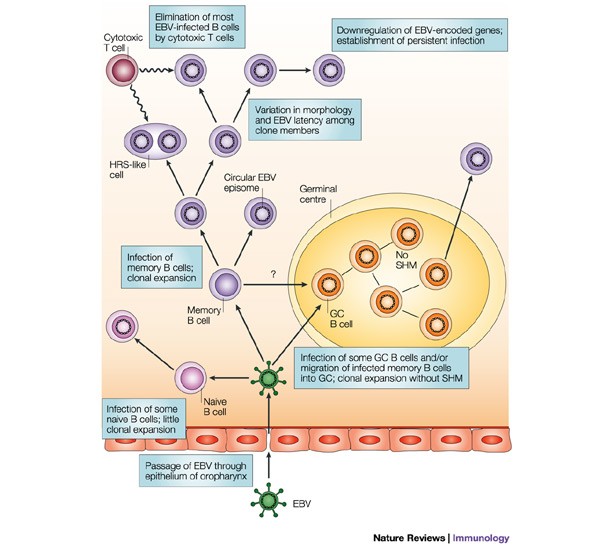
B cells under influence: transformation of B cells by Epstein–Barr virus | Nature Reviews Immunology
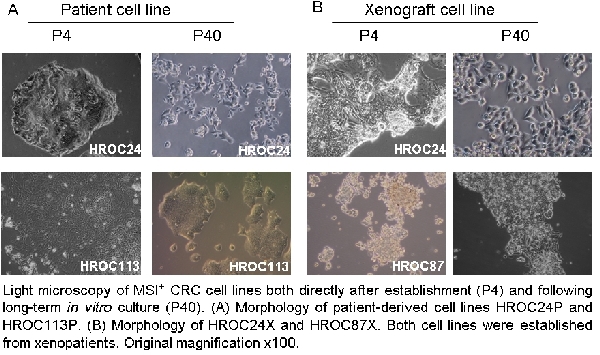
SSAT - Establishment and Characterization of Three Microsatellite-Instable Cell Lines Derived From Sporadic and Inherited Primary Colorectal Carcinomas

EBV transformation induces overexpression of hMSH2/3/6 on B lymphocytes and enhances γδT‐cell‐mediated cytotoxicity via TCR and NKG2D - Dai - 2018 - Immunology - Wiley Online Library
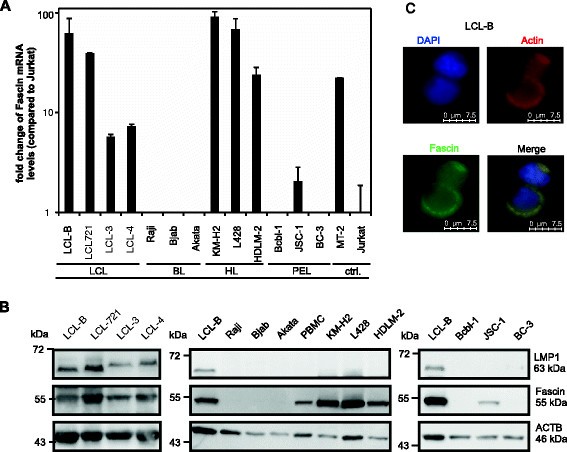
The tumor marker Fascin is induced by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded oncoprotein LMP1 via NF-κB in lymphocytes and contributes to their invasive migration | Cell Communication and Signaling | Full Text

EBV infection and direct transformation of B cells. EBV infects naive B... | Download Scientific Diagram

FasL+MHCII+ exosome production by EBV-transformed B-LCL. Epstein-Barr... | Download Scientific Diagram

Epstein–Barr virus reprograms human B lymphocytes immediately in the prelatent phase of infection | PNAS

Epstein-Barr Virus- (EBV-) Immortalized Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines (LCLs) Express High Level of CD23 but Low CD27 to Support Their Growth
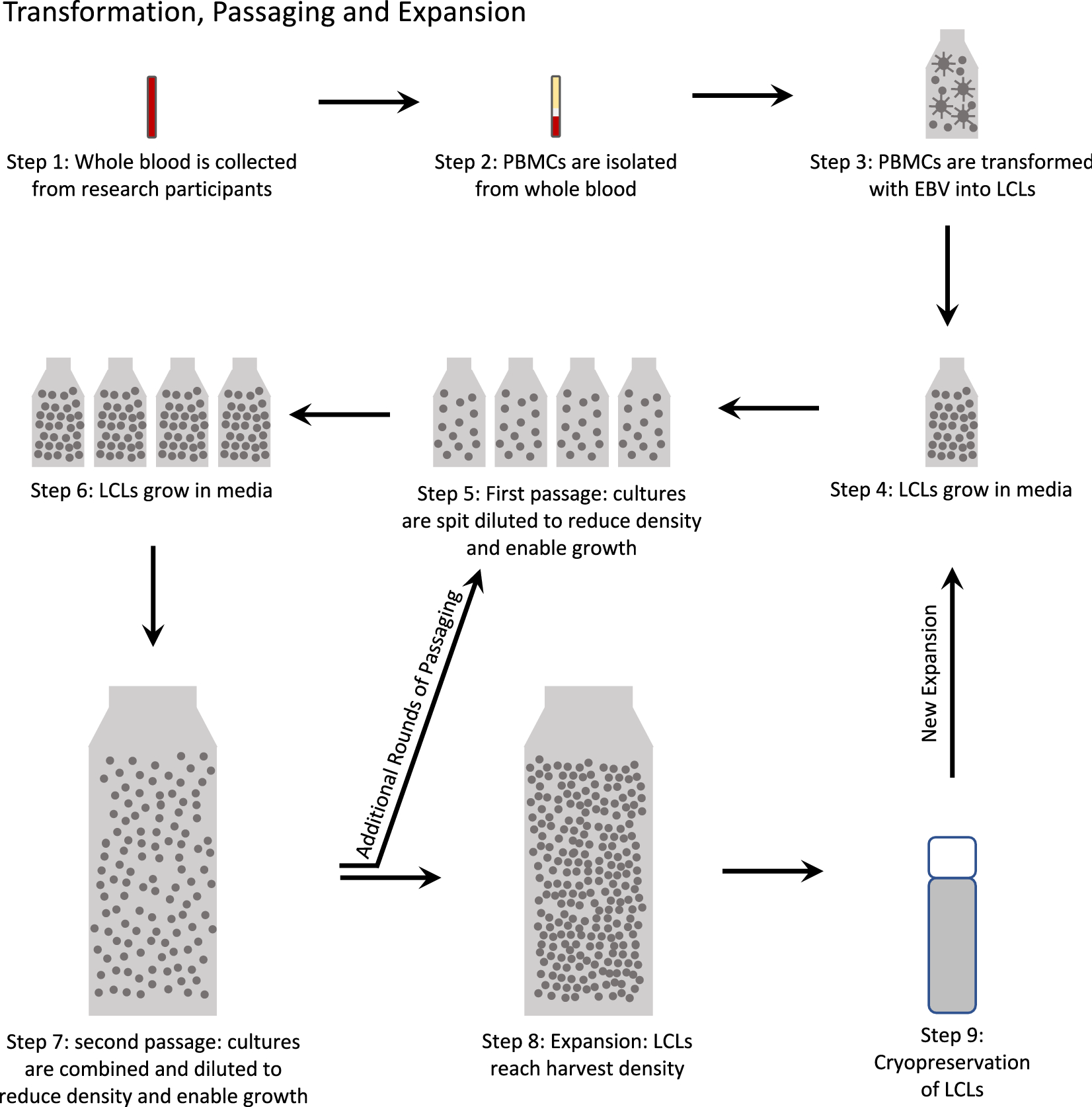
Genetic and genomic stability across lymphoblastoid cell line expansions | BMC Research Notes | Full Text
Epstein-Barr Virus Immortalization of Human B-Cells Leads to Stabilization of Hypoxia-Induced Factor 1 Alpha, Congruent with the Warburg Effect | PLOS ONE

Epstein-Barr Virus- (EBV-) Immortalized Lymphoblastoid Cell Lines (LCLs) Express High Level of CD23 but Low CD27 to Support Their Growth